About this Article
This article provides information related to Host Management associated with the profiles - the available monitoring modes, association/disassociation of Probes (VM only) and syncing them with the latest allowlist on CMS.
Monitoring Modes
The available Monitoring Modes for the hosts are:
Disabled - Host protection is not switched on
Detect - Executables that are not found in the host profile are reported immediately to CMS
The executables are not stopped from execution
If additional protection actions are configured in a protection profile, these actions are executed in response to a reported incident
Protect - Executables that are not found in the host profile are suspended/blocked immediately. They are not acted upon until the user adds the detected errant executable to the allowlist or deletes it on the CMS
In cases where the errant executable is added to the allowlist, the executable is resumed
In cases where the errant executable is deleted from the allowlist, the executable is killed
An executable not added to the allowlist on Windows is NOT allowed to execute
NOTE
Version 3.1 and Above: The protection modes can be configured independently for Executable (Host) Protection, ACP and Memory Exploit Protection
To modify the Host Monitoring mode:
On the Host Monitoring page, click the below icon
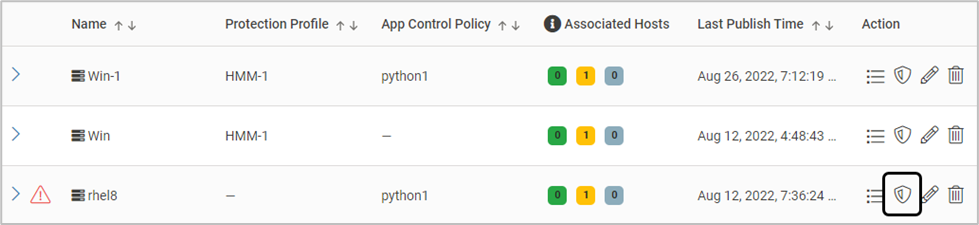
Select all the required hosts and click Manage Monitoring Mode.
The Mode can be chosen separately for Executable Protection, App Control Policy or Memory Exploit Protection
The Mode can be chosen for each host also. Select the required Monitoring Mode - Disable, Protect or Detect
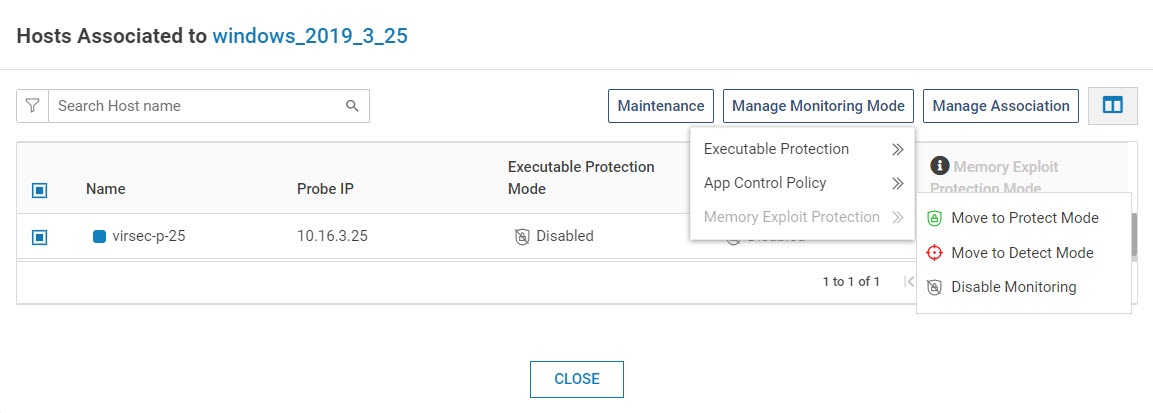
If the Probe version is 3.0.x, only the Executable Protection Mode is considered for all the three modes
Note that the ACP Monitoring can be in Protect Mode only if the Executable Protection is in Protect Mode. The Memory Exploit Protection Mode is independent of these two values
When ACP is configured to Protect Mode, Executable Protection is automatically configured to Protect Mode (if in Detect/Disable mode)
When Executable Protection is configured from Protect to Detect/Disable, ACP is automatically configured to Detect/Disable mode respectively
Here are the allowed values:
App Control Policy
Executable Protection
Disable
Protect
Disable
Detect
Disable
Disable
Detect
Protect
Detect
Detect
Detect
Disable
Protect
Protect
Select all the required hosts and click Manage Monitoring Mode. The Mode can be chosen for each host also. Select the required Monitoring Mode - Disable, Protect or Detect.
Associate/Disassociate Hosts (VMs only)
On the Host Monitoring page, click the below icon
The pop-up window displays the associated hosts. Click Manage Association > Associate
Hosts with the same OS type and Registered status are listed for profile association. Select the required hosts. Click ASSOCIATE. Click YES on the confirmation screen
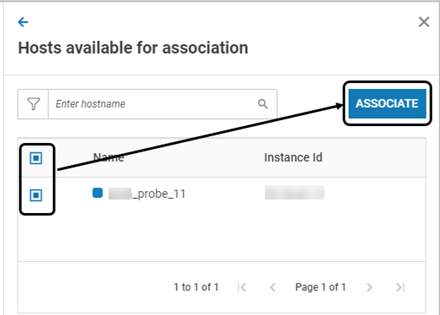
By default, the hosts are in Disabled mode after the association
Version 2.9 and Above: After association, a discovery scan is initiated on the newly associated host
Standard search options are available to view the required hosts
To disassociate hosts, select all the required hosts. Click Manage Association > Disassociate. Click YES on the confirmation screen
Mixed Mode (Linux only)
The Mixed mode feature allows VSP Host Protection to support 32-bit applications running on 64-bit Linux machines
By default, this feature is not enabled. Utilize the command below to enable it:
vsp-cli config hmm edit mixedMode trueMixed mode is not supported on all Linux Operating Systems. The supported OS are:
RHEL*
UBUNTU*
DEBIAN*
AMAZON-LINUX 1
SUSE
ORACLE LINUX
* Refer to the Compatibility Matrix of the corresponding VSP version for more information on the OS versions