About this Article
This article provides various options to monitor and track any detected attacks/threats by VSP Host Protection.
There are three ways to monitor Host Protection by VSP:
The widgets on the Dashboard provide a high-level view of the health of the associated hosts
Detected attacks/threats are reported as incidents in the CMS
Reports can be scheduled as and when required for any desired time frequency
Dashboard
Widgets like Hosts Process Classification, Host Script Execution and Top-N Affected Hosts provide real-time snapshots from the configured Hosts
The dashboard contains the below tiles:
App Control Violation - Depicts the number of ACP (App Control Policy) violations
Files Scanned - Depicts the number of Files Scanned
Host Protection Incidents
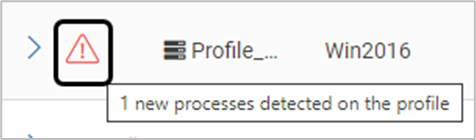
If one or more incidents are related to a profile or the associated libraries, they are displayed as shown below. Hover over the icon to view detailed information on the detected incidents. A click on the icon displays TrustGuardian > Incidents page with the list of incidents related to the profile
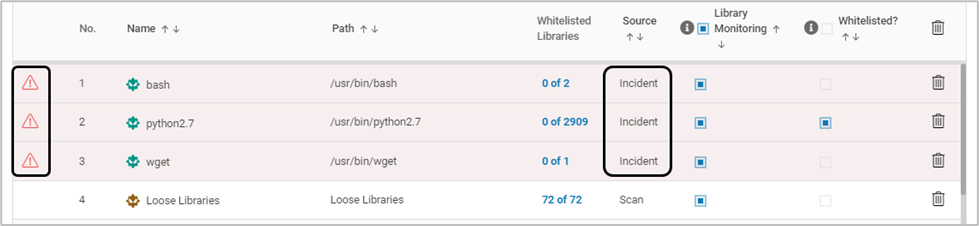
The incident can be viewed at the executable level also with the incident icon and the Source as Incident. A click on the icon displays the TrustGuardian > Incidents page with the list of incidents related to the executable
On Windows servers, when both Memory Exploit Protection and Library Monitoring are enabled in protect mode, for certain library injection attacks, MEP detects and kills the sourcing process (that is trying to inject a malicious library into a benign process). This attack is reported as a Memory Exploit Protection incident and NOT as a New Library incident
All the incidents are reported in the page TrustGuardian > Incidents
If one or more incidents are related to a profile or the associated libraries, they are displayed as shown below. Hover over the icon to view detailed information on the detected incidents. A click on the icon displays Monitor > Incidents page with the list of incidents related to the profile

The incident can be viewed at the executable level also with the incident icon and the Source as Incident. A click on the icon displays the Monitor > Incidents page with the list of incidents related to the executable

On Windows servers, when both Memory Exploit Protection and Library Monitoring are enabled in protect mode, for certain library injection attacks, MEP detects and kills the sourcing process (that is trying to inject a malicious library into a benign process). This attack is reported as a Memory Exploit Protection incident and NOT as a New Library incident
All the incidents are reported in the page Monitor > Incidents
Process related Incidents
There are two types of process incidents reported by VSP:
New Process – In situations where a new process is detected other than the allowlisted processes
Process Modified – In situations where a process name and path are the same, but a checksum mismatch is detected
If any script-hosting processes (like powershell, cscript.exe, wscript.exe, jscript.exe, python) is executed in detect mode, the command will complete its run. But if it is not a part of the allowlist, an incident is reported. It can be added to the allowlist if desired
Child Commands:
Common commands like ls, dir, ping, ipconfig can be executed along with powershell. No incidents will be reported on VSP and no executables need to be allowlisted
Whenever a command that invokes a child process is executed, two incidents – one for the parent process and another for the child process are reported
Commands like: -enc, -noP must be allowlisted before they are executed
The below truth table describes various scenarios and the type of incidents reported
Process Name | Process Path | Process Checksum | Incident Type |
|---|---|---|---|
No Match | Match | Match | No Incident |
No Match | Match | No Match | New Process |
No Match | No Match | No Match | No Incident |
No Match | No Match | No Match | New Process |
Match | Match | Match | No Incident |
Match | Match | No Match | Process modified |
Match | No Match | Match | No Incident |
Match | No Match | No Match | New Process |
Library related Incidents
There are three types of library monitoring incidents reported by VSP:
New Library – In situations where a new library is detected other than the allowlisted libraries
Library Modified – In situations where a library is allowlisted, but a checksum mismatch is detected
Library Hijack – In situations where a library is allowlisted, but a path mismatch is detected
The below truth table describes various scenarios and the type of incidents reported
Library Name | Library Path | Library Checksum | Incident Type |
|---|---|---|---|
No Match | Match | Match | No Incident |
No Match | Match | No Match | New Library |
No Match | No Match | Match | No Incident |
No Match | No Match | No Match | New Library |
Match | Match | Match | No Incident |
Match | Match | No Match | Library modified |
Match | No Match | Match | No Incident |
Match | No Match | No Match | Library Hijack |
ACP Incidents
While ACP violations (Fileless and Process Disallowed) are reported in the incident screen, they may not show a visual "warning" symbol in the Host Profile and Edit Allowlist screen
The script monitoring incidents are reported as “File-based Application Policy Violation” incidents
The various types of ACP incidents are:
Event Type | Description |
|---|---|
Access Control Violation | If a process is spawned on the configured host that violates the configured ACP rules under the section File-less Execution Rules > User Access Control, VSP generates an incident |
Child Process Violation | If a child process is spawned on the configured host while the ACP is configured to "block" under Dynamic Execution Rule, VSP generates an incident |
Command-line Violation | If a command is executed on the configured host that violates the configured ACP rules under the section File-less Execution Rules > Command Line, VSP generates an incident |
Parent Process Violation | If a process is spawned on the configured host that violates the configured ACP rules under the section File-less Execution Rules > Parent Process Control, VSP generates an incident |
Process Disallowed Violation | Whether a process is allowlisted or not, if Process Disallowed rule is created for it, ACP rule takes precedence over allowlisting. VSP blocks the process and generates an incident |
Script Monitoring | If a process is spawned on the configured host while the ACP is configured not to allow the file extension under File-based execution Rule, VSP generates an incident |
Reports
There are two reports that can be configured for Host Protection:
Suspended Processes Report – Provides detailed information about the protection actions carried out by VSP Host Monitoring feature on the enabled hosts
Host Monitoring Report – Provides detailed information related to all the process and library monitoring attacks along with ACP attacks detected for the configured hosts